Our Location
Index IT SAP St, Gayatri Nagar, Srinivasa Nagar,
Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500016
Phone: +91-8977802802
Email: indexit4sap@gmail.com
Index IT SAP St, Gayatri Nagar, Srinivasa Nagar,
Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Telangana - 500016
Phone: +91-8977802802
Email: indexit4sap@gmail.com
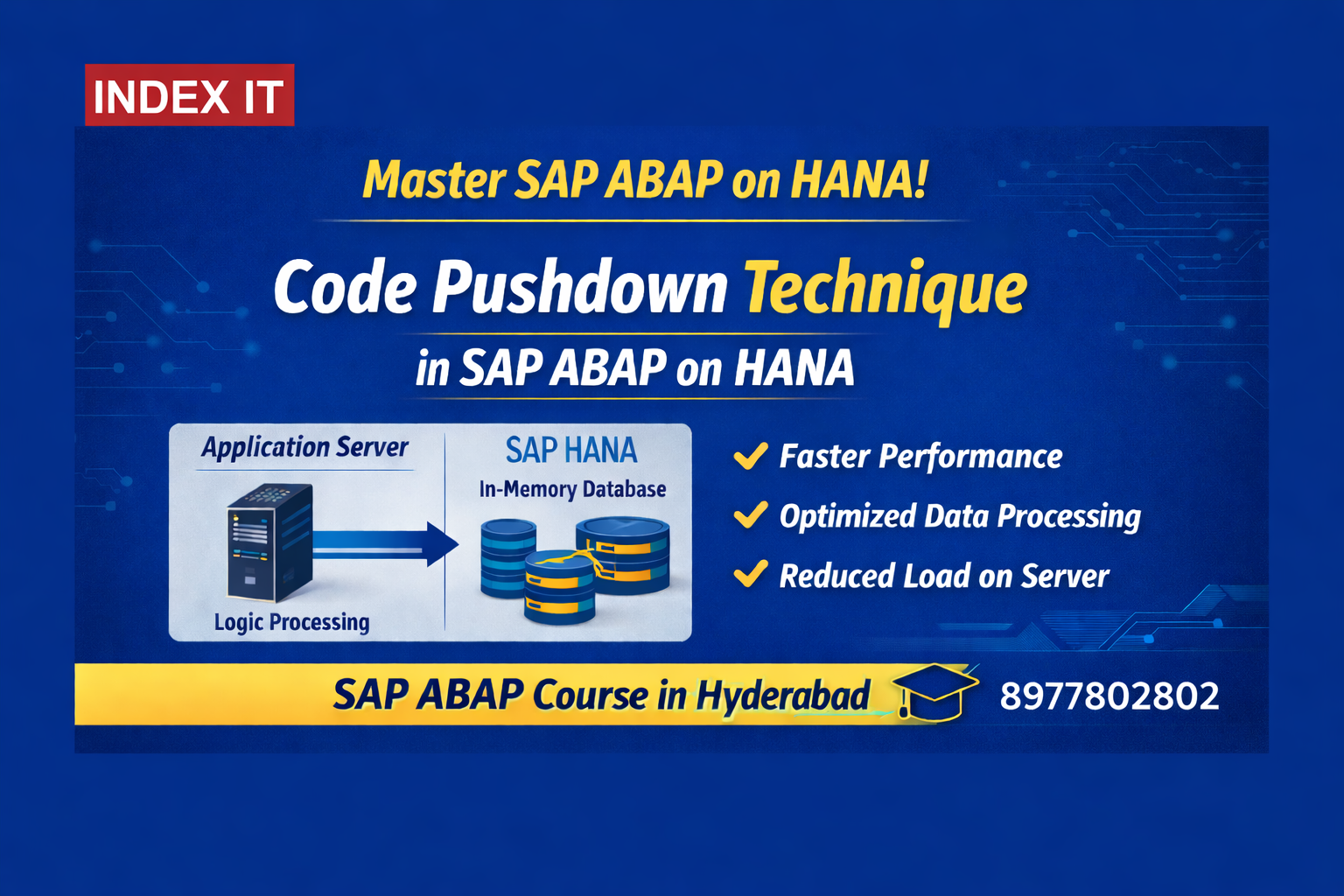
Learn Code Pushdown Technique in SAP ABAP on HANA with real-time training at Index IT – SAP ABAP Course in Hyderabad.
Modern SAP development has completely transformed after the introduction of SAP HANA and SAP BTP ABAP Environment.
If you are planning to build a career in S/4HANA or ABAP on Cloud, understanding Code Pushdown Technique and CDS Views is mandatory.
If you're looking for structured hands-on training, check our detailed SAP BTP ABAP Course in Hyderabad where we cover CDS, RAP, BTP, and real-time project implementation.
In classical ABAP:
When we fetch:
And display only 10 aggregated results…
We still:
This consumes:
This model is called:
With SAP HANA (In-Memory Database), SAP introduced a smarter and more efficient way of processing data.
Instead of:
We now:
This performance optimization concept is deeply explained in our 👉 SAP ABAP Course in Hyderabad with real-time project scenarios and detailed performance comparisons.
SAP provides three major approaches to implement Code Pushdown Technique in SAP ABAP on HANA:
Among these, CDS Views are the most widely used approach in S/4HANA and SAP BTP ABAP projects because they provide better performance, reusable data models, and seamless integration with Fiori and OData services.
CDS (Core Data Services) are a modern data modeling approach in SAP ABAP on HANA that enable developers to define and process business logic directly at the database layer.
CDS Views allow developers to:
CDS Views are created in:
CDS Views are not created in traditional SE11, as they are part of the modern ABAP development model optimized for SAP HANA.
In SAP ABAP on HANA, there are two ways to define Core Data Services:
Older Syntax:
DEFINE VIEW
New Recommended Syntax:
DEFINE VIEW ENTITY
If you're learning S/4HANA development, always focus on CDS View Entity, as it is the recommended and future-proof approach.
We teach both legacy and modern approaches in our 👉 SAP ABAP Course in Hyderabad so students can confidently handle real-time S/4HANA systems.
In SAP ABAP on HANA, CDS Views are categorized based on their purpose and usage. Understanding these types is extremely important for S/4HANA interviews and real-time project implementation.
SAP categorizes CDS Views into different layers based on how the data is modeled, combined, and consumed in applications like Fiori, OData, and Analytics.
Interface Views are the foundation layer in CDS architecture. They directly expose database tables or basic business logic.
Naming Convention Example: I_SalesOrder, I_Product
Composite Views combine multiple interface views or tables and apply additional business logic such as joins, filters, and aggregations.
Consumption Views are created for front-end usage such as SAP Fiori, OData Services, and Analytics.
Naming Convention Example: C_SalesReport
Private Views are used internally by SAP and are not intended for direct customer consumption.
💡 Interview Tip: Always explain CDS layering as Interface → Composite → Consumption when answering S/4HANA interview questions.
| Feature | Classic ABAP | CDS / Code Pushdown |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Layer | Application Server | Database Layer (HANA) |
| Data Transfer | Large dataset fetched | Only final result fetched |
| Performance | Slower for large volumes | Optimized & Faster |
| Aggregation | Handled in LOOP | Handled in Database (SUM, GROUP BY) |
| Memory Usage | High | Low |
| Future Relevance | Legacy approach | S/4HANA Standard |
🚀 In modern S/4HANA and SAP BTP ABAP projects, Code Pushdown using CDS Views is the recommended and performance-optimized approach.
Code Pushdown Technique is an optimization approach where business logic is executed at the database layer (SAP HANA) instead of the application server, improving performance and reducing data transfer.
CDS (Core Data Services) Views are modern data modeling objects in SAP ABAP on HANA that allow developers to define semantic data models and push processing logic to the database layer.
CDS View Entity is the modern recommended syntax that does not create a separate SQL view, offering better maintainability and alignment with S/4HANA development standards.
CDS Views are important because they enable high-performance applications by utilizing SAP HANA’s in-memory processing and support Fiori, OData, and analytics integration.
